Causes and Cures for Red and Itchy Vaginal Bumps

Vaginal Bumps and Itches: Is It an STD?
There
are many causes for itchy bumps on the vagina (or, to be exact, on the
vulva, mons pubis, labia, or external parts of the vagina). The first
thing a woman thinks of is a sexually transmitted disease. Although that
is an understandable fear, often there is another explanation for these
symptoms.
Itchy vaginal bumps are symptoms that are similar to those of some STDs or STIs (sexually transmitted infections). This makes it challenging to determine the culprit. Women should see their gynecologist for an accurate diagnosis of these bumps. However, if the vaginal bumps are not sexually transmitted, some simple over-the-counter remedies will cure or alleviate many cases.
Note: This article is about bumps that itch. Although there are many other reasons one might develop a bump on the vagina, we're narrowing our focus on the causes of the ones that itch, starting with the most harmless and least alarming.
Itchy vaginal bumps are symptoms that are similar to those of some STDs or STIs (sexually transmitted infections). This makes it challenging to determine the culprit. Women should see their gynecologist for an accurate diagnosis of these bumps. However, if the vaginal bumps are not sexually transmitted, some simple over-the-counter remedies will cure or alleviate many cases.
Note: This article is about bumps that itch. Although there are many other reasons one might develop a bump on the vagina, we're narrowing our focus on the causes of the ones that itch, starting with the most harmless and least alarming.

Vaginal / Vulval Acne: Vaginal pimples are like face pimples or those found elsewhere on the body. | Source
Are Daily Habits Causing Vaginal Acne?
Cause:
Acne is most often the cause of bumps that are red and itchy on and around the vagina. Vaginal pimples are like face pimples, or those found elsewhere on the body. Vaginal acne is skin's natural reaction to harsh soap, douches, shaving or not showering enough. In teen and early adult years, this area may have excessive secretions—sweat or oil— which may clog the pores and lead to pimples. Wearing tight underwear made of synthetic or non-absorbent material can trap this moisture and cause acne as well.
Cure:
You can treat vaginal acne by cleaning the area with warm water (without soap) several times daily. Keep the area clean and dry and wear cotton underwear. Don't try to pop or squeeze the pimple. This will cause irritation, and possibly lead to infection. A warm compress might help.
Extreme conditions of vaginal acne may require medical attention for treatment with cortisone injections or other means.
Acne is most often the cause of bumps that are red and itchy on and around the vagina. Vaginal pimples are like face pimples, or those found elsewhere on the body. Vaginal acne is skin's natural reaction to harsh soap, douches, shaving or not showering enough. In teen and early adult years, this area may have excessive secretions—sweat or oil— which may clog the pores and lead to pimples. Wearing tight underwear made of synthetic or non-absorbent material can trap this moisture and cause acne as well.
Cure:
You can treat vaginal acne by cleaning the area with warm water (without soap) several times daily. Keep the area clean and dry and wear cotton underwear. Don't try to pop or squeeze the pimple. This will cause irritation, and possibly lead to infection. A warm compress might help.
Extreme conditions of vaginal acne may require medical attention for treatment with cortisone injections or other means.

An ingrown hair. Sometimes, you can see the hair under the surface. | Source
Could That Vaginal Bump Be an Ingrown Hair?
It
looks like a pimple (a red bump on the skin, varying in size, sometimes
with pus inside), it feels like a pimple (painful and itchy), but it
isn't a pimple, it's an ingrown hair.
Cause:
Ingrown hairs are those that have somehow curled and grown sideways or back down into your skin instead of exiting. One common type of ingrown hair is called pseudofolliculitis, also known as razor bumps, a group of small bumps that appear after you've shaved, waxed, or tweezed. Because the hair is cut so short, it gets turned around and trapped under the surface of your skin.
This may happen more often to people with thick or curly hair. Also, it can happen if something clogs the pores and prevents the hair from growing out—for example, dead skin can clog a hair follicle, as can excessive sweat or certain products.
Cure:
Usually, this bump will eventually heal itself. If you're prone to ingrown hairs, exfoliating (gently scrubbing away dead skin), using a sharp razor when shaving, shaving in the direction the hair is growing, switching to another method of hair removal or letting the hair grow can all help.
If it doesn't heal itself, an ingrown hair may become infected. It may darken the skin or leave a scar, especially if you've been picking or scratching. If this happens, your doctor can make a small incision to get it out. Your doctor may also prescribe something to help.
Cause:
Ingrown hairs are those that have somehow curled and grown sideways or back down into your skin instead of exiting. One common type of ingrown hair is called pseudofolliculitis, also known as razor bumps, a group of small bumps that appear after you've shaved, waxed, or tweezed. Because the hair is cut so short, it gets turned around and trapped under the surface of your skin.
This may happen more often to people with thick or curly hair. Also, it can happen if something clogs the pores and prevents the hair from growing out—for example, dead skin can clog a hair follicle, as can excessive sweat or certain products.
Cure:
Usually, this bump will eventually heal itself. If you're prone to ingrown hairs, exfoliating (gently scrubbing away dead skin), using a sharp razor when shaving, shaving in the direction the hair is growing, switching to another method of hair removal or letting the hair grow can all help.
If it doesn't heal itself, an ingrown hair may become infected. It may darken the skin or leave a scar, especially if you've been picking or scratching. If this happens, your doctor can make a small incision to get it out. Your doctor may also prescribe something to help.
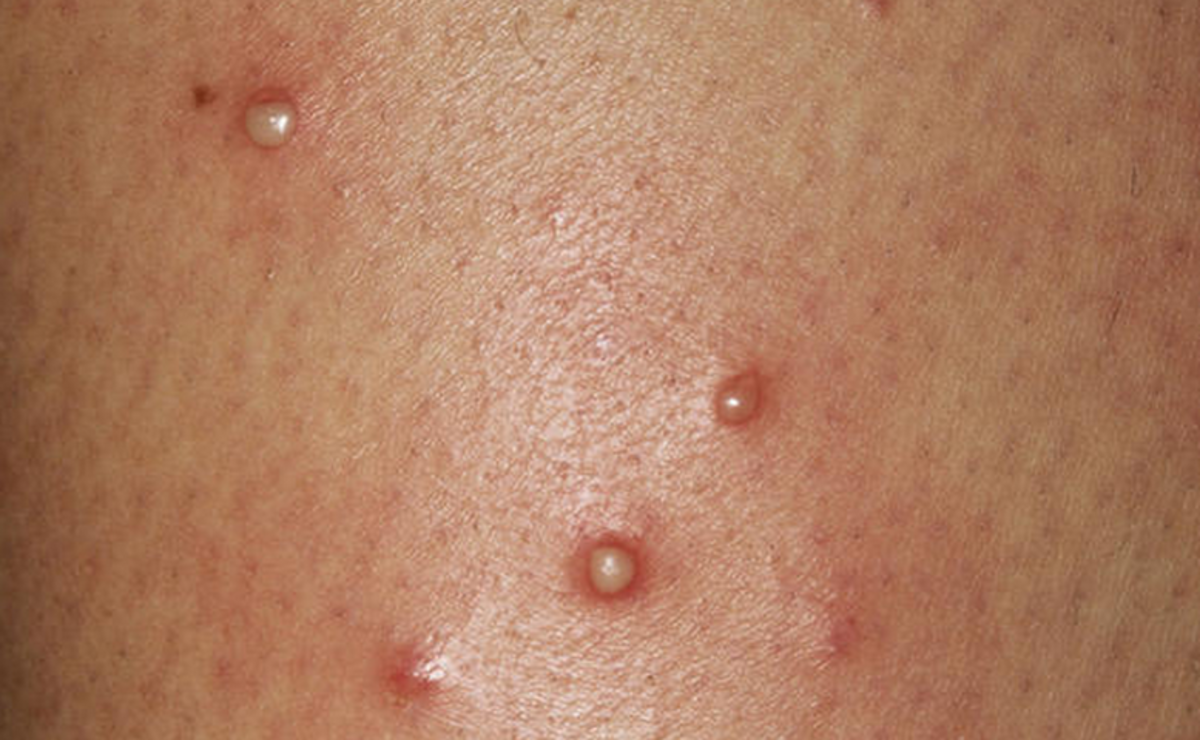
Vaginal Folliculitis might look like this: It begins as small red
bumps or whiteheads and develops into infected, crusty sores. | Source
Could It Be Folliculitis?
Folliculitis
is an extremely common skin condition, and is one of the most common
forms of bumps found in the genital area. It is caused by hair follicles
that have become inflamed, often leading to a bacterial or fungal
infection. It begins as small red bumps or whiteheads, and develops into
infected, crusty sores.
Cause:
Folliculitis is caused by sweat or friction from clothing that blocks a hair follicle on or around the vagina. The resulting bumps may become infected.
Cure:
Folliculitis usually heals on its own in approximately two weeks. If it is a small, singular bump, it can be treated by placing a warm compress on the area three times a day. A saltwater solution may also offer relief. If there are multiple bumps, recurring bumps, or if a bump doesn't heal, a trip to the doctor for an incision, drainage and antibiotic or antifungal may be required.
Cause:
Folliculitis is caused by sweat or friction from clothing that blocks a hair follicle on or around the vagina. The resulting bumps may become infected.
Cure:
Folliculitis usually heals on its own in approximately two weeks. If it is a small, singular bump, it can be treated by placing a warm compress on the area three times a day. A saltwater solution may also offer relief. If there are multiple bumps, recurring bumps, or if a bump doesn't heal, a trip to the doctor for an incision, drainage and antibiotic or antifungal may be required.
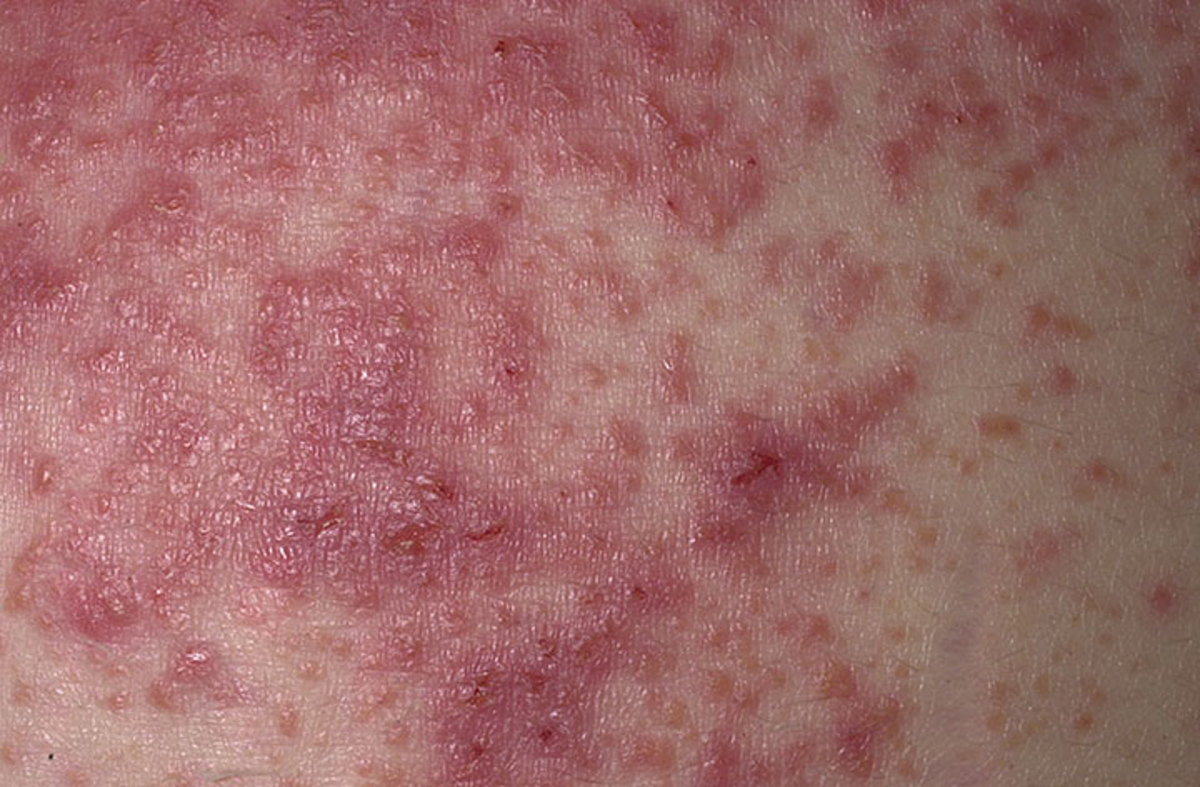
This is what eczema might look like. Look for redness, minute
papules or vesicles (that look like pimples) which might be weeping,
oozing, or crusting. | Source
Could It Be Eczema?
Another
cause of itchy, red vaginal bumps is eczema (aka atopic dermatitis).
Eczema is "a general term for any superficial inflammatory process
involving the epidermis, marked early by redness, itchiness, minute
papules and vesicles, weeping, oozing and crusting."
Cause:
We don't know exactly what causes it (although it is believed to be caused by a combination of environmental and hereditary factors) and, unfortunately, we don't know a cure. For many, it is a recurrent and painful disease they will have to deal with for the rest of their lives.
Cure:
There is no cure, but it can be treated. Your gynecologist may prescribe external topical corticosteroids, but they have some extreme side effects. Discomfort might also be alleviated with a variety of home remedies including using a cool compress or soaking in baths, followed by a moisturizing lotion regimen. Use a cream with natural ingredients and no added perfume or fragrance. Aloe vera might be applied two or three times a day, but you'll want to watch to see how your skin responds. Adjusting eating habits along with stress reduction are also helpful in minimizing recurrence. Yogurt and acidophilus capsules have also been used to varying degrees of success.
Be careful not to scratch eczema bumps or the itchiness will intensify and the eczema will spread. These remedies may sound simple enough, but eczema is a tough culprit to clear up. It is essential to follow treatment advice on a daily basis.
Cause:
We don't know exactly what causes it (although it is believed to be caused by a combination of environmental and hereditary factors) and, unfortunately, we don't know a cure. For many, it is a recurrent and painful disease they will have to deal with for the rest of their lives.
Cure:
There is no cure, but it can be treated. Your gynecologist may prescribe external topical corticosteroids, but they have some extreme side effects. Discomfort might also be alleviated with a variety of home remedies including using a cool compress or soaking in baths, followed by a moisturizing lotion regimen. Use a cream with natural ingredients and no added perfume or fragrance. Aloe vera might be applied two or three times a day, but you'll want to watch to see how your skin responds. Adjusting eating habits along with stress reduction are also helpful in minimizing recurrence. Yogurt and acidophilus capsules have also been used to varying degrees of success.
Be careful not to scratch eczema bumps or the itchiness will intensify and the eczema will spread. These remedies may sound simple enough, but eczema is a tough culprit to clear up. It is essential to follow treatment advice on a daily basis.

Molluscum Contagiosum: Smooth, round bumps of varying size, with a
central indentation, firm to the touch, and filled with a waxy
substance. | Source
Maybe It's a Viral Infection (Molluscum Contagiosum)?
Molluscum
contagiosum is a virus that spreads through close skin-to-skin contact,
including but not limited to sexual contact. In the vaginal area, this
virus appears in the form of smooth and shiny round bumps of varying
size, with a central indentation. They are firm to the touch and filled
with a waxy substance. The bumps appear in varied colors ranging from
white, pink, red and other flesh tones, and are often itchy, swollen,
and sore.
Cause:
Any activity that involves touching an infected person's bumps, touching the hand that scratched those bumps, or even contact with an infected towel or piece of clothing may expose you to the virus.
Cure:
They usually disappear on their own, but it may take months. However, if you are sexually active or worried about exposing someone else, treatment will shorten the healing time. Your doctor may treat them with dry ice, topical cream, or laser removal.
Cause:
Any activity that involves touching an infected person's bumps, touching the hand that scratched those bumps, or even contact with an infected towel or piece of clothing may expose you to the virus.
Cure:
They usually disappear on their own, but it may take months. However, if you are sexually active or worried about exposing someone else, treatment will shorten the healing time. Your doctor may treat them with dry ice, topical cream, or laser removal.
Causes and Cures for Red and Itchy Vaginal Bumps
![Causes and Cures for Red and Itchy Vaginal Bumps]() Reviewed by Unknown
on
19:09:00
Rating:
Reviewed by Unknown
on
19:09:00
Rating:
